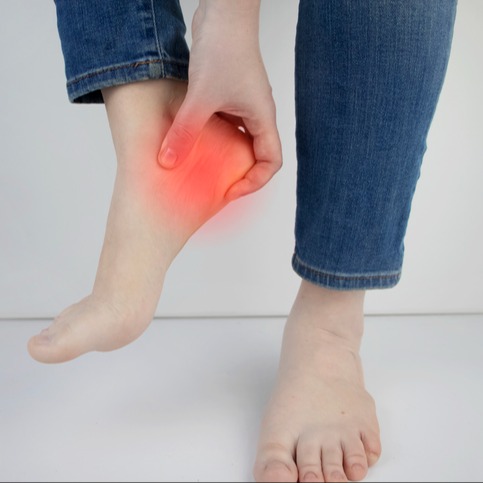
Fascite plantare
La fascite plantare rappresenta una tra le cause più comuni di dolore al tallone. Si tratta dell’infiammazione di una fascia (fascia plantare) di tessuto, che attraversa la parte inferiore del piede e collega l’osso del calcagno alla parte anteriore del piede.
Si tratta di una patologia ortopedica, comunemente nota sotto forma di un dolore lancinante, che di solito si manifesta con i primi passi al mattino. Appena alzati e dopo aver compiuto i primi passi della giornata, il dolore generalmente diminuisce, ma potrebbe ripresentarsi dopo lunghi periodi trascorsi in piedi o quando ci si alza dopo essersi seduti.
Approfondimenti
 Cause
Cause
La causa della fascite plantare è poco conosciuta. È più comune nei corridori e nelle persone in sovrappeso.
La fascia plantare è una fascia di tessuto (fascia) che collega l'osso del tallone alla base delle dita dei piedi. Supporta l'arco del piede e assorbe gli urti durante la camminata. La tensione e lo stress sulla fascia possono causare piccoli strappi. Lo stiramento e lo strappo ripetuti della fascia possono irritarla o infiammarla, sebbene in molti casi di fascite plantare la causa rimanga poco chiara.
Anche se la fascite plantare può svilupparsi senza una causa evidente, alcuni fattori possono aumentare il rischio di sviluppare questa condizione. Tra questi, troviamo:
- età. La fascite plantare è più comune nelle persone di età compresa tra 40 e 60 anni;
- alcuni tipi di esercizi. Le attività che sottopongono molto stress al tallone e ai tessuti annessi, come la corsa su lunghe distanze, la danza classica e la danza aerobica, possono contribuire all'insorgenza della fascite plantare;
- meccanica del piede. I piedi piatti, un arco plantare alto o anche un modello di camminata atipico possono influenzare il modo in cui viene distribuito il peso quando si sta in piedi e possono sottoporre a ulteriore stress la fascia plantare;
- obesità. I chili in eccesso mettono a dura prova la fascia plantare;
- occupazioni che ti tengono in piedi. Gli operai, gli insegnanti e tutti coloro che trascorrono la maggior parte del loro orario di lavoro camminando o stando in piedi su superfici dure possono essere maggiormente a rischio di fascite plantare.
 Sintomi
Sintomi
La fascite plantare provoca in genere un dolore lancinante nella parte inferiore del piede vicino al tallone. Il dolore è solitamente più intenso con i primi passi dopo il risveglio, anche se può essere scatenato anche da lunghi periodi in piedi o quando ci si alza dalla posizione seduta.
 Diagnosi
Diagnosi
La diagnosi si basa su un esame clinico, condotto solitamente dallo specialista ortopedico e da una diagnostica per immagini, tramite ecografia del piede o risonanza per visualizzare la fascia plantare.
L'esame ecografico è preferibile, perché è a basso costo. Esso è sufficiente per fare diagnosi per immagini e consente, tramite doppler, di valutare la vascolarizzazione di ogni zona della fascia plantare.
In alcuni casi, possono venire richiesti esami diagnostici aggiuntivi per fare diagnosi differenziale, o escludere patologie concomitanti, ad esempio tramite la radiografia o l'elettromiografia.
 Rischi
Rischi
Sottovalutare la fascite plantare può causare un dolore cronico a carico del tallone, rendendo difficile lo svolgimento delle attività ordinarie. È possibile che si modifichi la tua camminata, in modo da evitare il dolore da fascite plantare, che potrebbe arrecare problemi al piede, al ginocchio, all'anca o alla schiena.
 Cure e Trattamenti
Cure e Trattamenti
La fascite plantare si cura, solitamente, tramite un approccio conservativo e, solo nei casi meno responsivi, tramite un approccio chirurgico.
L'approccio conservativo prevede:
- farmaci (cortisonici per bocca o per infiltrazione locale, antinfiammatori per bocca, integratori);
- terapia fisica (fisioterapia con stretching della fascia plantare e del tendine di Achille, onde d'urto, laserterapia);
- ortesi podologiche (plantari, talloniere di rialzo).
L'approccio chirurgico prevede:
- tecniche mininvasive rx-guidate o eco-guidate, come il release parziale della fascia plantare, a cui si può o meno associare l'asportazione della spina calcaneare inferiore, se presente;
- infiltrazioni di concentrato piastrinico (PRP) o cellule mesenchimali autologhe;
- tecniche classiche come la fasciotomia parziale a cielo aperto o in mini-open.
Bibliografia
- López-López D., Pérez-Ríos M., Ruano-Ravina A., Losa-Iglesias M.E., Becerro-de-Bengoa-Vallejo R., Romero-Morales C., Calvo-Lobo C., Navarro-Flores E. Impact of quality of life related to foot problems: A case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:14515. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93902-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Dunn J.E., Link C.L., Felson D.T., Crincoli M.G., Keysor J.J., McKinlay J.B. Prevalence of foot and ankle conditions in a multiethnic community sample of older adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2004;159:491–498. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwh071. - DOI - PubMed.
- Hill C.L., Gill T.K., Menz H.B., Taylor A.W. Prevalence and correlates of foot pain in a population-based study: The North West Adelaide health study. J. Foot Ankle Res. 2008;1:2. doi: 10.1186/1757-1146-1-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Riddle D.L., Schappert S.M. Volume of ambulatory care visits and patterns of care for patients diagnosed with plantar fasciitis: A national study of medical doctors. Foot Ankle Int. 2004;25:303–310. doi: 10.1177/107110070402500505. - DOI - PubMed.
- Sobhani S., Dekker R., Postema K., Dijkstra P.U. Epidemiology of ankle and foot overuse injuries in sports: A systematic review. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports. 2013;23:669–686. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0838.2012.01509.x. - DOI - PubMed.
- Lopes A.D., Hespanhol Júnior L.C., Yeung S.S., Costa L.O. What are the main running-related musculoskeletal injuries? A Systematic Review. Sports Med. 2012;42:891–905. doi: 10.1007/BF03262301. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Wearing S.C., Smeathers J.E., Urry S.R., Hennig E.M., Hills A.P. The pathomechanics of plantar fasciitis. Sports Med. 2006;36:585–611. doi: 10.2165/00007256-200636070-00004. - DOI - PubMed.
- Ostermann S., Olesen J.L., Holden S., Riel H. Stretching and relaxing the plantar fascia may change plantar fascia thickness but not pressure pain thresholds: A cross-sectional study of patients with plantar fasciopathy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020;21:804. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03833-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Melo S.N.S., Ezekwesili A., Yurdi N.A., Murrell W.D., Maffulli N. Gold-Induced Cytokine (GOLDIC(®)) Injection Therapy in Patient with Plantar Fasciosis: A Case Report. Indian J. Orthop. 2020;54:348–351. doi: 10.1007/s43465-020-00089-4. - DOI - PMC – PubMed.
- Franchini M., Cruciani M., Mengoli C., Marano G., Pupella S., Veropalumbo E., Masiello F., Pati I., Vaglio S., Liumbruno G.M. Efficacy of platelet-rich plasma as conservative treatment in orthopaedics: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Blood Transfus. 2018;16:502–513. doi: 10.2450/2018.0111-18. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Andia I., Maffulli N. Muscle and tendon injuries: The role of biological interventions to promote and assist healing and recovery. Arthroscopy. 2015;31:999–1015. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2014.11.024. - DOI - PubMed.
- Tsikopoulos K., Tsikopoulos A., Natsis K. Autologous whole blood or corticosteroid injections for the treatment of epicondylopathy and plantar fasciopathy? a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Phys. Ther. Sport. 2016;22:114–122. doi: 10.1016/j.ptsp.2016.02.002. - DOI - PubMed.
- Singh P., Madanipour S., Bhamra J.S., Gill I. A systematic review and meta-analysis of platelet-rich plasma versus corticosteroid injections for plantar fasciopathy. Int. Orthop. 2017;41:1169–1181. doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3470-x. - DOI - PubMed.
- Yang W.Y., Han Y.H., Cao X.W., Pan J.K., Zeng L.F., Lin J.T., Liu J. Platelet-rich plasma as a treatment for plantar fasciitis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine. 2017;96:e8475. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008475. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Chen Y.J., Wu Y.C., Tu Y.K., Cheng J.W., Tsai W.C., Yu T.Y. Autologous Blood-Derived Products Compared with Corticosteroids for Treatment of Plantar Fasciopathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2019;98:343–352. doi: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000001070. - DOI - PubMed.
- Huang K., Giddins G., Wu L.D. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Corticosteroid Injections in the Management of Elbow Epicondylitis and Plantar Fasciitis: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020;48:2572–2585. doi: 10.1177/0363546519888450. - DOI - PubMed.
- Mohammed W., Farah S., Nassiri M., McKenna J. Therapeutic efficacy of platelet-rich plasma injection compared to corticosteroid injection in plantar fasciitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Orthop. 2020;22:124–134. doi: 10.1016/j.jor.2020.03.053. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Hohmann E., Tetsworth K., Glatt V. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Corticosteroids for the Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2021;49:1381–1393. doi: 10.1177/0363546520937293. - DOI - PubMed.
- Alkhatib N., Salameh M., Ahmed A.F., Alkaramany E., Ahmed G., Mekhaimar M.M., Alsaei J. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Corticosteroids in the Treatment of Chronic Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Prospective Comparative Studies. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2020;59:546–552. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2019.10.003. - DOI - PubMed.
- Hurley E.T., Shimozono Y., Hannon C.P., Smyth N.A., Murawski C.D., Kennedy J.G. Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Corticosteroids for Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2020;8:2325967120915704. doi: 10.1177/2325967120915704. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Tseng W.C., Uy J., Chiu Y.H., Chen W.S., Vora A. The Comparative Effectiveness of Autologous Blood-derived Products Versus Steroid Injections in Plantar Fasciitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. PMR. 2021;13:87–96. doi: 10.1002/pmrj.12373. - DOI - PubMed.
- Speed C. A systematic review of shockwave therapies in soft tissue conditions: Focusing on the evidence. Br. J. Sports Med. 2014;48:1538–1542. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2012-091961. - DOI - PubMed.
- Sun J., Gao F., Wang Y., Sun W., Jiang B., Li Z. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy is effective in treating chronic plantar fasciitis: A meta-analysis of RCTs. Medicine. 2017;96:e6621. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006621. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Al-Abbad H., Allen S., Morris S., Reznik J., Biros E., Paulik B., Wright A. The effects of shockwave therapy on musculoskeletal conditions based on changes in imaging: A systematic review and meta-analysis with meta-regression. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020;21:275. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-03270-w. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Ogden J.A., Alvarez R.G., Marlow M. Shockwave therapy for chronic proximal plantar fasciitis: A meta-analysis. Foot Ankle Int. 2002;23:301–308. doi: 10.1177/107110070202300402. - DOI - PubMed.
- Thomson C.E., Crawford F., Murray G.D. The effectiveness of extra corporeal shock wave therapy for plantar heel pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2005;6:19. doi: 10.1186/1471-2474-6-19. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Al-Boloushi Z., López-Royo M.P., Arian M., Gómez-Trullén E.M., Herrero P. Minimally invasive non-surgical management of plantar fasciitis: A systematic review. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2019;23:122–137. doi: 10.1016/j.jbmt.2018.05.002. - DOI - PubMed.
- Salvioli S., Guidi M., Marcotulli G. The effectiveness of conservative, non-pharmacological treatment, of plantar heel pain: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Foot. 2017;33:57–67. doi: 10.1016/j.foot.2017.05.004. - DOI - PubMed.
- Hsiao M.Y., Hung C.Y., Chang K.V., Chien K.L., Tu Y.K., Wang T.G. Comparative effectiveness of autologous blood-derived products, shock-wave therapy and corticosteroids for treatment of plantar fasciitis: A network meta-analysis. Rheumatology. 2015;54:1735–1743. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev010. - DOI - PubMed.
- Tsikopoulos K., Vasiliadis H.S., Mavridis D. Injection therapies for plantar fasciopathy (‘plantar fasciitis’): A systematic review and network meta-analysis of 22 randomised controlled trials. Br. J. Sports Med. 2016;50:1367–1375. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2015-095437. - DOI - PubMed.
- Li X., Zhang L., Gu S., Sun J., Qin Z., Yue J., Zhong Y., Ding N., Gao R. Comparative effectiveness of extracorporeal shock wave, ultrasound, low-level laser therapy, noninvasive interactive neurostimulation, and pulsed radiofrequency treatment for treating plantar fasciitis: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Medicine. 2018;97:e12819. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012819. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Li H., Lv H., Lin T. Comparison of efficacy of eight treatments for plantar fasciitis: A network meta-analysis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018;234:860–870. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26907. - DOI - PubMed.
- Drake C., Mallows A., Littlewood C. Psychosocial variables and presence, severity and prognosis of plantar heel pain: A systematic review of cross-sectional and prognostic associations. Musculoskelet. Care. 2018;16:329–338. doi: 10.1002/msc.1246. - DOI - PubMed.
- Anderson M.J., Browning W.M., 3rd, Urband C.E., Kluczynski M.A., Bisson L.J. A Systematic Summary of Systematic Reviews on the Topic of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2016;4:2325967116634074. doi: 10.1177/2325967116634074. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Jancuska J., Matthews J., Miller T., Kluczynski M.A., Bisson L.J. A Systematic Summary of Systematic Reviews on the Topic of the Rotator Cuff. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2018;6:2325967118797891. doi: 10.1177/2325967118797891. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- de Sa D., Lian J., Sheean A.J., Inman K., Drain N., Ayeni O., Mauro C. A Systematic Summary of Systematic Reviews on the Topic of Hip Arthroscopic Surgery. Orthop. J. Sports Med. 2018;6:2325967118796222. doi: 10.1177/2325967118796222. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Jomaa G., Kwan C.-K., Fu S.-C., Ling S.K.-K., Chan K.-M., Yung P.S.-H., Rolf C. A systematic review of inflammatory cells and markers in human tendinopathy. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2020;21:78. doi: 10.1186/s12891-020-3094-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed.
- Baksh N., Hannon C.P., Murawski C.D., Smyth N.A., Kennedy J.G. Platelet-rich plasma in tendon models: A systematic review of basic science literature. Arthroscopy. 2013;29:596–607. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2012.10.025. - DOI - PubMed.
- Yan R., Gu Y., Ran J., Hu Y., Zheng Z., Zeng M., Heng B.C., Chen X., Yin Z., Chen W., et al. Intratendon Delivery of Leukocyte-Poor Platelet-Rich Plasma Improves Healing Compared with Leukocyte-Rich Platelet-Rich Plasma in a Rabbit Achilles Tendinopathy Model. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017;45:1909–1920. doi: 10.1177/0363546517694357. - DOI - PubMed.
- Cross J.A., Cole B.J., Spatny K.P., Sundman E., Romeo A.A., Nicholson G.P., Wagner B., Fortier L.A. Leukocyte-Reduced Platelet-Rich Plasma Normalizes Matrix Metabolism in Torn Human Rotator Cuff Tendons. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015;43:2898–2906. doi: 10.1177/0363546515608157. - DOI - PubMed.
- Fitzpatrick J., Bulsara M., Zheng M.H. The Effectiveness of Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Tendinopathy: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials. Am. J. Sports Med. 2017;45:226–233. doi: 10.1177/0363546516643716. - DOI - PubMed.
- Deluca S., Robinson D.M., Yun P.H., Rosenberg C., Tan C.O., Tenforde A.S. Similar Functional Gains Using Radial versus Combined Shockwave Therapy in Management of Plantar Fasciitis. J. Foot Ankle Surg. 2021;60:1098–1102. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2021.04.013. - DOI - PubMed.
- Johnson C.D., Tenforde A.S., Outerleys J., Reilly J., Davis I.S. Impact-Related Ground Reaction Forces Are More Strongly Associated with Some Running Injuries than Others. Am. J. Sports Med. 2020;48:3072–3080. doi: 10.1177/0363546520950731. - DOI - PubMed.
- Malliaras P., Barton C.J., Reeves N.D., Langberg H. Achilles and patellar tendinopathy loading programmes: A systematic review comparing clinical outcomes and identifying potential mechanisms for effectiveness. Sports Med. 2013;43:267–286. doi: 10.1007/s40279-013-0019-z. - DOI - PubMed.
- Jones I.A., Togashi R.C., Thomas Vangsness C., Jr. The Economics and Regulation of PRP in the Evolving Field of Orthopedic Biologics. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2018;11:558–565. doi: 10.1007/s12178-018-9514-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed. Leggi altro...
L'informazione presente nel sito deve servire a migliorare, e non a sostituire, il rapporto medico-paziente. In caso di disturbi e/o malattie rivolgiti al tuo medico di base o ad uno specialista.
Cerca i migliori specialisti che si occupano di Fascite plantareRevisione Scientifica

Trova il Medico più adatto alle tue esigenze.